Home » Cashless Payments Knowledge Hub » Enjoy Seamless Verifications and Transactions with Our Leveraged NFC Technology

NFC (Near Field Communication) is a comparatively short wireless networking technology based on standards that are increasingly being used in consumer and professional electronics, notably for integrating mobile devices as a way of sharing digital content. Users can use Near Field Communication (NFC) technology to make secure transactions, share digital data and content, and connect electronic devices with a single tap. NFC broadcasts have a small range (from a few centimeters to a few inches) and require the devices to be close together.
Near-field communication allows two devices to communicate by transmitting data using electromagnetic radio signals. Because transactions take place over such a short distance, both devices must have NFC chips. To transfer data, NFC-enabled devices must be physically touching or within a few millimeters of each other.
Near-field communications (NFCs) considerably reduce the likelihood of human error because the receiving device reads your data as soon as you provide it. You may rest comfortably, for example, that a pocket-dial or strolling past a site with an NFC chip will not allow you to make an unintentional transaction (called a “smart poster”). You must conduct an action consciously when using near-field communication.
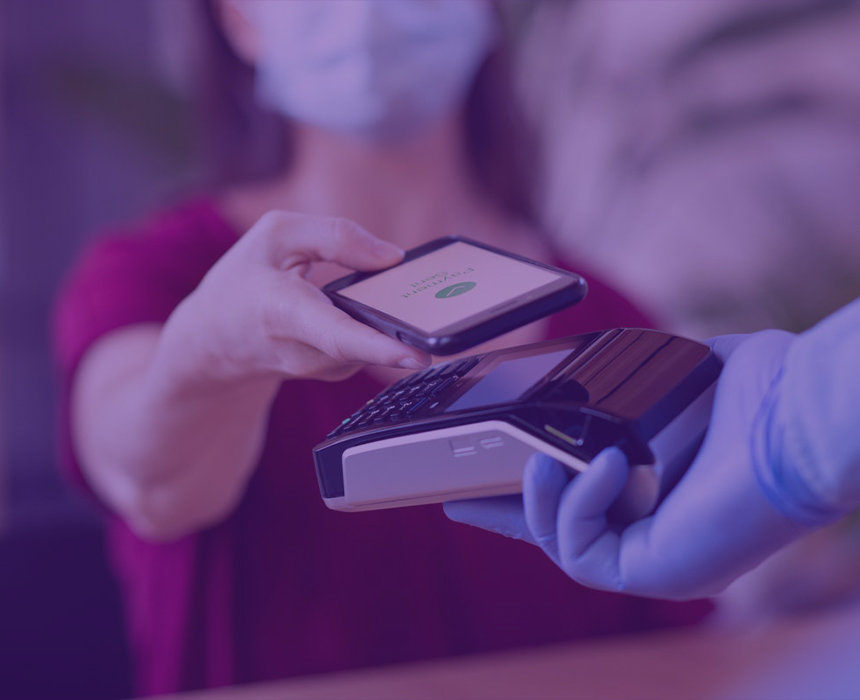
NFC mobile payments are contactless payments that process payments through NFC communication. They are used widely to verify consumers’ data and make payments with smartphones and smartwatches by using mobile wallets and tapping to pay credit and debit cards.
Using this type of contactless payment method is very similar to using a credit card with a magnetic stripe to make a payment. However, instead of reading the magnetic stripe, the radio signal initiates the transaction.
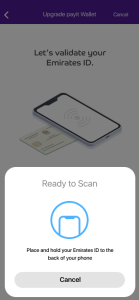
Definitely, payit supports an advanced NFC technology and now all new payit users can enjoy seamless identity verification to verify their new accounts as their identification information is read electronically from Emirates ID through the new leveraged identity verification solution powered by Near-Field Communication (NFC) technology to allow secure identity verification at the highest level, reduce identity fraud, and create a safe digital environment.


The technology is deceptively simple: an NFC chip, which emerged from radio frequency identification (RFID) technology, functions as one component of a wireless link. When activated by another chip, modest quantities of data can be exchanged between the two devices when they are kept a few centimeters apart.
It doesn’t require a pairing code to connect, and it’s significantly more power-efficient than other wireless communication kinds since it employs processors that run on extremely low power (or passively, requiring even less).
NFC’s main goal is to identify us using our equipped cards and devices (and by extension, our bank accounts, and other personal info.)
NFC mobile payments are most likely the world’s most convenient payment method. Paying with your phone is quick, secure, and simple. To make a payment with your smartphone, place it close to the NFC receiver (e.g., a terminal, a card reader). As previously stated, NFC devices communicate via radio signals.
When the two devices are in close proximity, the NFC chips encrypt the data and transmit it to the receiver. Encryption is used on both ends to ensure that payments are as secure as possible. Furthermore, the customer must authorize the transaction with a passcode, fingerprint, or face ID.
When the transaction is approved, the funds are transferred to the merchant’s terminal using a randomly generated single-use code that is sent to the merchant. As a result, each transaction is highly secure and safe from hackers.
NFC is capable of three modes of operation:
NFC payments use a variety of security measures to keep all data safe. They are as follows:
If you’ve ever wondered why NFC payments are so popular, it’s because of their numerous advantages. Because they are faster, more convenient, and more secure, they outperform both Bluetooth and EMV. But let’s take a closer look at its advantages:
NFC payments are quick because they do not require communication and verification between the sending and receiving devices, as EMV transactions do. After tapping on your phone, money is transferred from your smartphone to the receiver in a matter of seconds. When compared to EMV transactions, this allows for much faster transactions. And, if you work with a large number of people and don’t want to see long lines in front of the counter, speed is everything. Furthermore, faster payments equal more sales!
As previously stated, NFC payments employ a variety of security measures to ensure secure payments. Before transferring the data to the receiving device, mobile wallets encrypt it. Some use traditional encryptions, while others, such as Apple Pay, tokenize your bank information, rendering it unusable. Furthermore, the tokens change with each transaction, making them impossible to extract. Furthermore, before making a payment, some mobile wallets require a fingerprint or face ID authorization.
Using mobile wallets to pay is extremely convenient. To pay, simply bring your phone close to an NFC reader (such as a terminal) and tap on your phone. Furthermore, NFC payments use less power, allowing you to use this technology in passive devices such as tags without powering them up.
Accepting NFC mobile payments strengthens and deepens merchant-customer relationships. This is since they both get what they want: convenient, quick, and secure transactions. On the one hand, customers have a higher level of trust in the merchants and will return again and again. On the other hand, merchants can more effectively integrate customer loyalty programs into payment processing. Customers, for example, can redeem a coupon by simply tapping their phones. Furthermore, these programs assist merchants in collecting useful data about their customers, which allows them to determine the success of their program and, if necessary, improve it.
Mobile NFC Payments Are Here to Stay Regardless of consumer and merchant concerns. The main reason for this is the Covid-19 pandemics, which resulted in a 40% increase in contactless payments. And, it appears, they will continue to use contactless and NFC payments after the pandemic has passed.